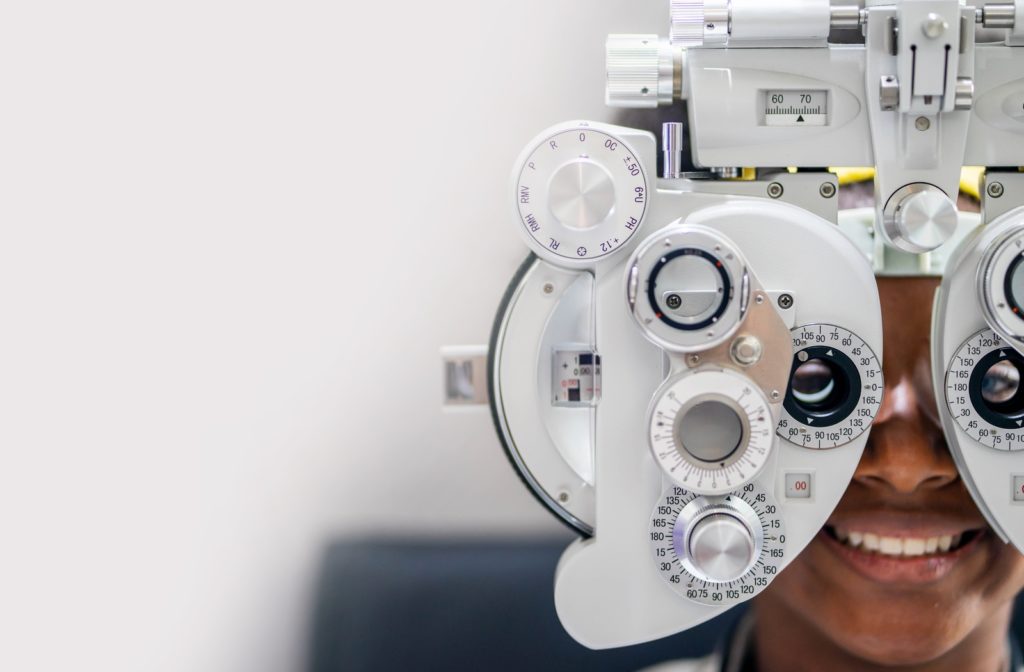
Eye exams are an important part of caring for your vision and overall eye health. A comprehensive eye exam is an opportunity to learn the best practices for maintaining and managing eye care. With a variety of tools and methods, a comprehensive eye exam is essential for preventative health care.
Unlike a screening, which only checks vision, a comprehensive eye exam is a thorough examination. As a result, the process can provide a more accurate diagnosis and monitor for problems that have no obvious signs or symptoms.
Regular comprehensive eye exams can help protect your ocular health. Adults should schedule an eye exam every 2 years. Those with a higher risk of ocular problems should come in every year.
What Is Included In A Comprehensive Eye Exam?
Case History
The first part of a comprehensive eye exam is gathering patient history. Your optometrist can get a clearer picture of your health by discussing your medical history, family medical history, and lifestyle habits.
We have better insight into your unique eye care needs with more information. Knowing more about the entire picture makes it easier to answer your health questions.
Preliminary Tests
Preliminary tests measure multiple aspects of your ocular system. During these tests, an eye care professional checks depth perception, color vision, peripheral vision, muscle movements, and pupil reactions.
The Snellen eye chart is the classic letter chart that checks visual acuity. The test evaluates the clarity of your vision, measured as a fraction. For example, normal vision is 20/20, indicating what the average person can see standing 20 feet away from the eye chart.
A visual field test assesses peripheral vision. Each eye is evaluated individually, using a center fixation light with blinking test lights appearing intermittently in your side vision. The results indicate how far and how sensitive our field of vision is without moving our eyes. The test can also signify if your vision is affected by injury or disease, such as glaucoma.
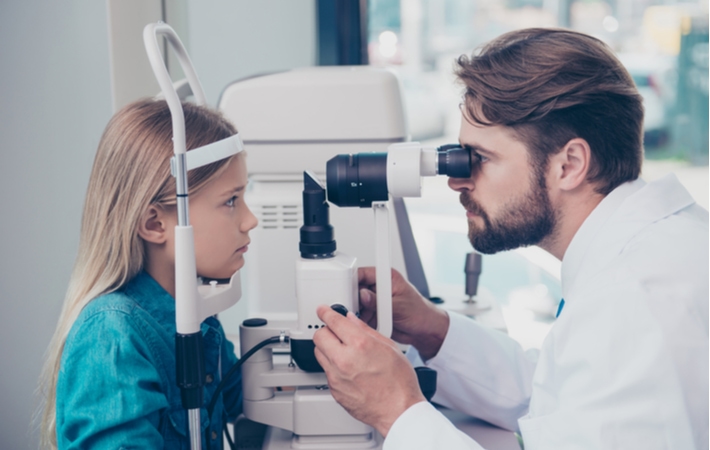

Eye Health Evaluation
In addition to your vision, eye health also includes eye tissues, structures, and intraocular pressure. Eye health is examined through a variety of tools, including microscopes, lenses, digital technology, and other diagnostic equipment.
Both the inner and outer eyes are part of an eye health evaluation. Not all tools and tests are used universally, as the individual examiner will decide what methods are available or necessary.
DRI and OCT
Digital retinal imaging (DRI) and ocular coherence tomography (OCT) use noninvasive methods to measure your eye. Both tests are tools for diagnosing several ocular conditions, including glaucoma, age-related eye diseases, macular degeneration (MD), and diabetic eye disease.
Digital retinal imaging provides clear images of your retina, optic nerve, and the back of your eye.
Ocular coherence tomography uses imaging to create cross-sections of your retina. The images provide your optometrist with a detailed view of your retina and optic nerve layers.
Dilating eye drops are sometimes used to widen the pupil, making it easier to examine inside the eye.
Precise measurements of your eye shape are also crucial in determining the best fit for contact lenses.
Refraction Test
An essential part of our vision is light refraction. When light enters our eyes through the cornea and lens, sometimes the shape of our eye can result in a refractive error. Examining the shape of your eyes determines if a refraction error is affecting your vision.
Types of refraction errors include hyperopia (farsightedness), myopia (nearsightedness), astigmatism, and presbyopia.
A light is shone into each eye individually during the refraction test to assess the amount of light reflected. The results of a refraction test determine a prescription if corrective eyewear is necessary.
How Long Is A Comprehensive Eye Exam?
The length of a comprehensive eye exam can vary depending on your eye care needs. Each test can take between 5–10 minutes. Most optometrists complete eye exams in an hour.
Who Should Get A Comprehensive Eye Exam?
A comprehensive eye exam is the best way to stay informed about your eye health. Your ocular system can provide insights into your vision and your overall health. With a detailed eye care evaluation, patients have a more in-depth understanding. You’re empowered to make more informed choices about your health.
Patients of any age can benefit from a comprehensive eye exam. Adults should book an appointment biennially. Children’s eye exams follow alternative guidelines, with annual comprehensive exams recommended starting before first grade.